5 Easy Facts About From Inspiration to Creation: A Journey into Understanding How Ideas Form in our Brains Described

Mapping Innovation: Understanding the Neural Pathways of the Creative Mind
Innovation is a sensation that has intrigued experts, performers, and thinkers throughout history. It is the capacity to generate new ideas, solve troubles in innovative methods, and generate authentic works of fine art. But what goes on inside the brain when we are being innovative? How do This Is Cool provide to this process? In this blog message, we will discover the principle of mapping ingenuity and explore right into the interesting world of the artistic mind.
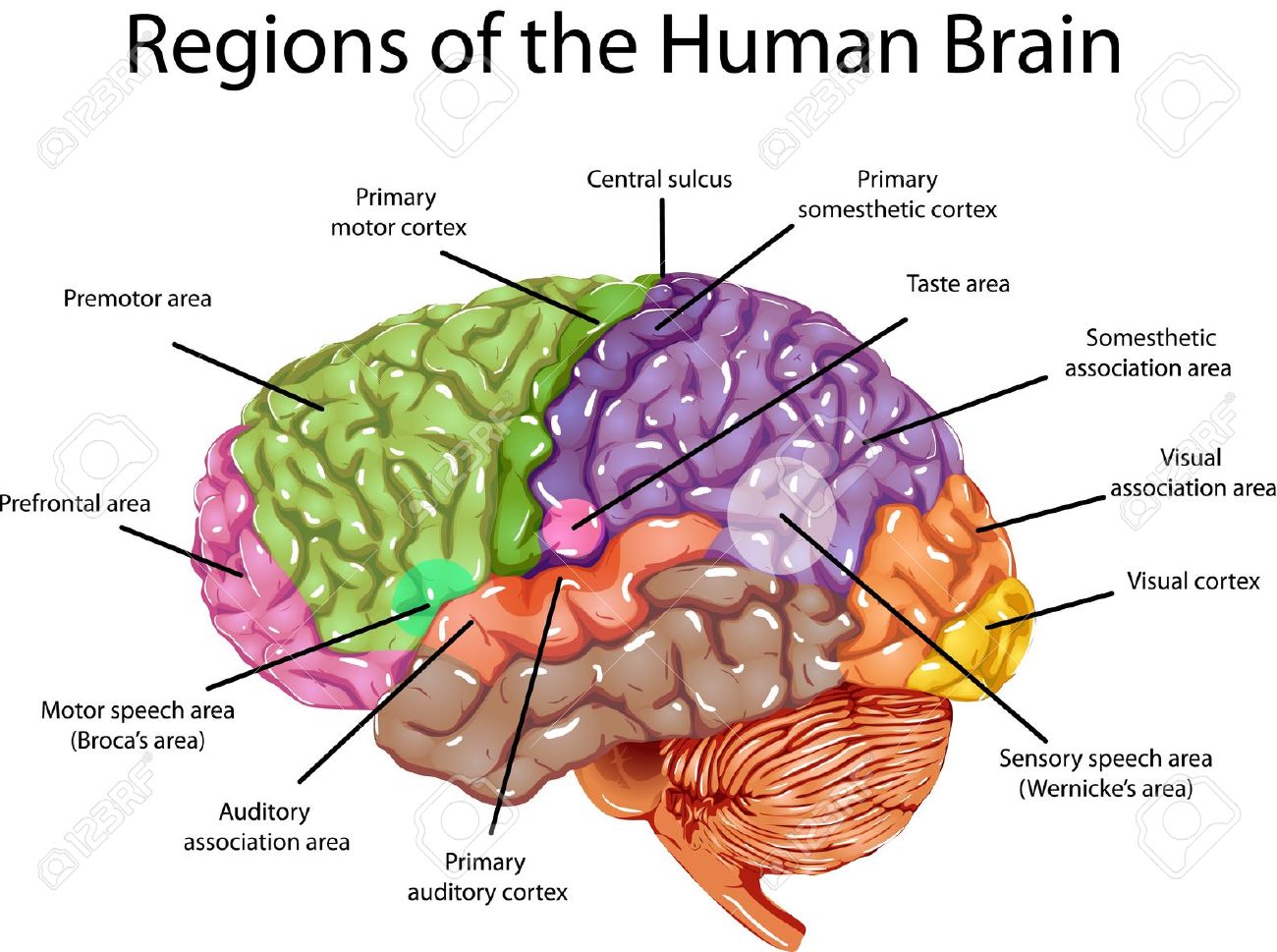
The individual brain is a complicated network of billions of interconnected cells called neurons. These nerve cells communicate with each other through power impulses and chemical indicators, creating elaborate paths known as neural networks. It is within these systems that ingenuity takes form.
Neuroscientists have long been studying how various regions of the human brain provide to imaginative thinking. One area that has obtained significant interest is the prefrontal peridium, which plays a vital part in much higher cognitive feature such as problem-solving, decision-making, and imagination. Researches have presented that damage to this area can easily badly harm a person's capability to assume creatively.
One more key player in imagination is the default mode network (DMN), a set of brain regions that come to be energetic when our minds are at remainder or involved in spontaneous thought. The DMN has been shown to be involved in generating suggestions, castle in the air, and making hookups between relatively unrelated principles – all important parts of creative thinking.
Current advancements in neuroimaging procedures like functional magnetic vibration image resolution (fMRI) have made it possible for analysts to map out these nerve organs process linked with innovation much more exactly. By scanning individuals' brains while they involve in various artistic activities such as drawing or brainstorming, scientists can easily determine which locations are even more energetic during these activities.
One research administered through scientists at Stanford University intended to uncover how different types of innovation switch on distinctive neural networks. Attendees were asked to finish duties involving either creative creative thinking (e.g., drawing) or different thinking (e.g., happening up with numerous remedies to a concern). The outcome presented that artistic ingenuity mostly involved the aesthetic and motor regions of the human brain, while divergent thinking triggered locations affiliated along with cognitive management and interest.
Remarkably, research study has also shown that certain aspects may affect the neural paths of ingenuity. For instance, studies have discovered that state of mind may influence imaginative thinking. Beneficial emotional states like joy and happiness and pleasure have been presented to boost creative problem-solving capabilities, while adverse emotions like unhappiness or temper may impede them. This proposes that the state of our mental well-being directly influences how our brains involve in imaginative processes.
Furthermore, scientists have discovered that certain people possess what is known as "improved innovation." These individuals display a greater level of variant thinking and are much more very likely to happen up with initial tips reviewed to others. Neuroimaging studies on these very imaginative individuals have showed structural and functional distinctions in their brains reviewed to those with ordinary or below-average creativity. These findings suggest that there might be a hereditary part at play in identifying one's innovative potentials.
Understanding the nerve organs pathways of creativity not just offers beneficial insights right into how our brains function but additionally has sensible effects. By acquiring a far better understanding of how innovation unfolds in the brain, we may be capable to build approaches to improve it even further. This know-how might benefit a broad range of areas such as learning, advancement, and therapy for individuals along with innovative blockages.
In conclusion, applying creative thinking includes unraveling the detailed nerve organs process within our brains that add to this outstanding phenomenon. Studying these paths may aid us understand the rooting mechanisms behind individual ingenuity and dropped illumination on why some individuals are even more naturally artistic than others. By delving deeper right into this amazing target, we might uncover new methods of nurturing and encouraging innovation in ourselves and others.
Referrals:
1. Dietrich A., & Kanso R.. (2010). A evaluation of EEG, ERP, and neuroimaging research studies of innovation and insight. Mental Bulletin, 136(5), 822–848.
2. Jung, R. E., & Vartanian, O. (2018). The Cambridge Handbook of the Neuroscience of Creativity. Cambridge University Press.
3. Takeuchi H., et al. (2010). Regional grey matter volume of dopaminergic device affiliate along with imagination: Documentation from voxel-based morphometry; Human Brain Mapping, 31(3), 398-409.
4. Ueda Y., et al. (2019). Neural Correlates Underlying Mood Effects on Innovative Thinking: Evidence from an fMRI Research; Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 13, 1-12.
